Body
Get to know your body through a better understanding of your anatomy and find the answers to some of your most common questions.
Back
All topics

4 resources
19 resources

6 resources

4 resources

6 resources
Back
All topics

9 resources

12 resources

4 resources

11 resources

2 resources
Back
Back
All topics
17 resources
11 resources
13 resources

2 resources

Mauj Products
We’ve designed our products to help you explore your body, solo or otherwise. Whether you’re a curious novice or a seasoned explorer, this is for you.
Back
All topics

4 resources

19 resources

6 resources

4 resources

6 resources
Back
All topics

9 resources

12 resources

4 resources

11 resources

2 resources
Back
Back
All topics

17 resources

11 resources

13 resources

2 resources

Mauj Products
We’ve designed our products to help you explore your body, solo or otherwise. Whether you’re a curious novice or a seasoned explorer, this is for you.

A Pap smear is an extremely important medical test used to detect abnormal cells in the cervix, which is the lower part of your uterus. It’s used to identify early signs of cervical cancer, allowing for timely intervention and prevention. It is also used to screen for the presence of the human papillomavirus (HPV).
Every woman aged 21 and above, regardless of her sexual history, should be getting tested regularly. Doctors typically advise repeating it every three years for women aged 21 to 65, assuming the initial test results are normal. However, if any abnormalities were detected in your first test, your healthcare provider may suggest more frequent screenings.
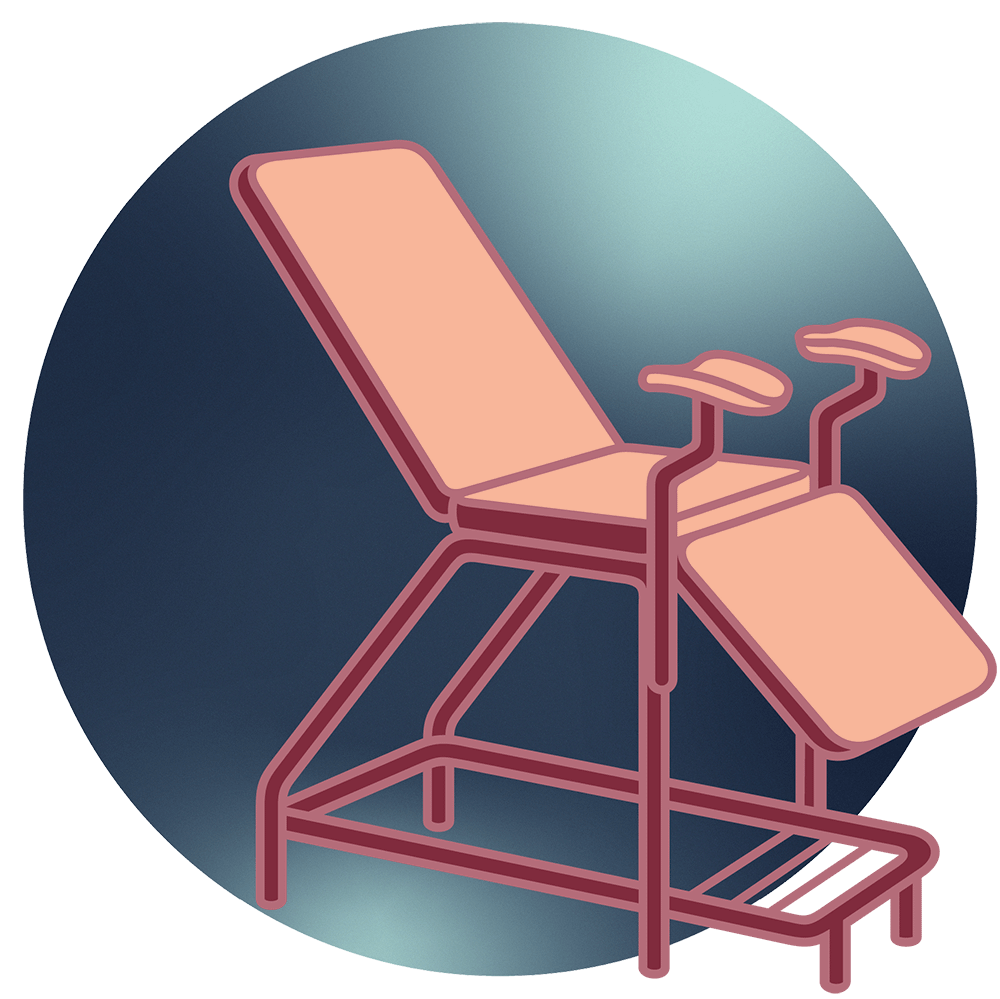

You will be asked to undress from the waist down and lie on an examination table with your feet placed in stirrups. You’ll be provided a drape or sheet for modesty.
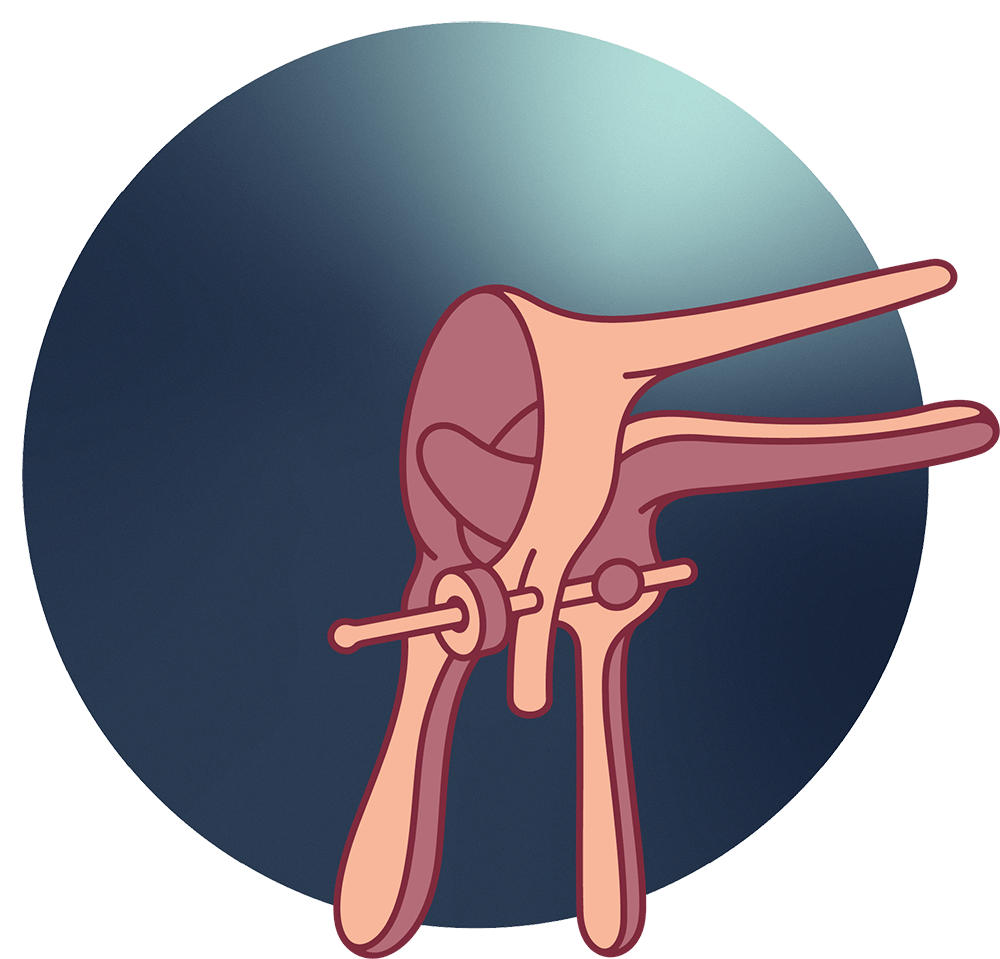
Your healthcare provider will ask you to open your legs and will gently insert a speculum (the medical tool shown above) into your vagina to widen the vaginal walls, allowing them to see the cervix clearly. It may feel uncomfortable, but it shouldn’t be painful. Communicate any pain to your healthcare provider.
It helps to relax as much as possible during this step. Take deep breaths and try to relax your vaginal muscles.
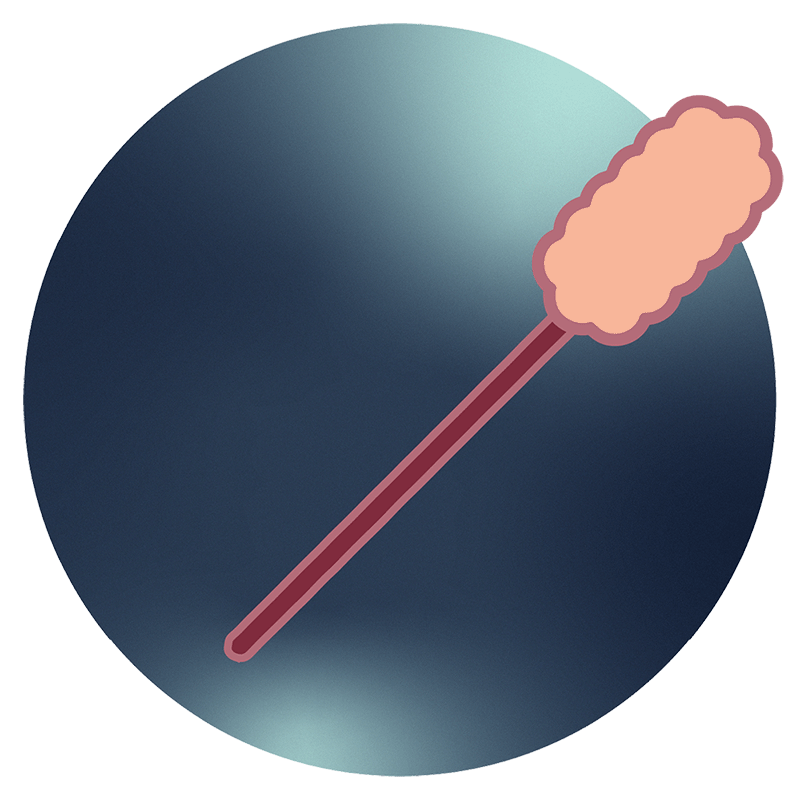
Using a small brush or swab, your healthcare provider will collect a sample of cells from the cervix. This process is quick and typically painless. You may feel a sensation of pressure or mild discomfort.
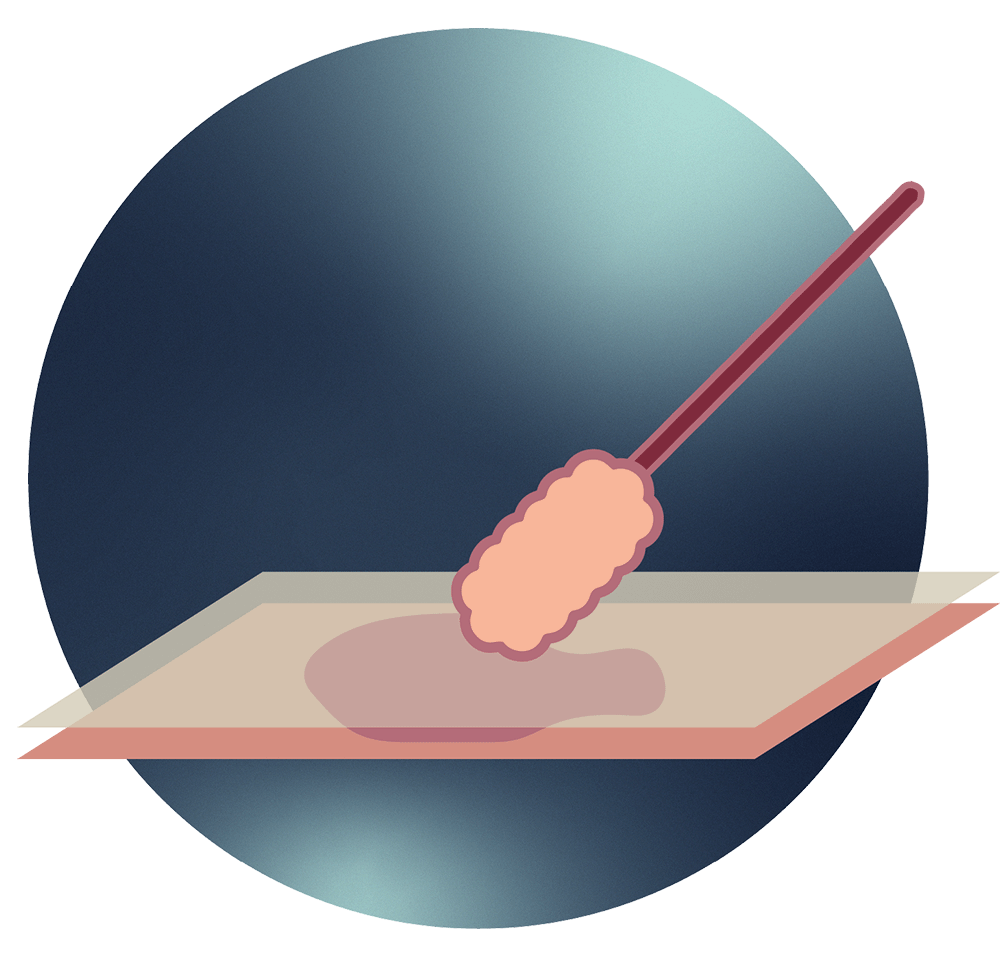
The collected cells are then placed on a glass slide or in a liquid solution and sent to a laboratory for analysis. The speculum is gently removed and the procedure is complete.
Always remember that you can and have the right to ask your healthcare provider about the process before you start. You can ask them to talk you through each step as they're performing it.
Did you find the answer you were looking for? Is there something we missed? What did you think of this resource? We want to hear from you.





